Exploring the Potential of 8 Essential Analysis Functions
Message Transmission
Message Monitoring
Bus Statistics
Bus logging
Message Playback
Video Playback
Graphical Curves & Numerical Displays
Database
- Manual, shortcut key, and periodic message sending options.
- Signal generator creates sine, square, triangle waves, and custom patterns.
- Add custom messages or pull from the database.
- Copy messages to C scripts for flexible sending.
- Display absolute and relative time.
- Choose between scrolling and fixed display modes.
- Instantly view signal values with DBC parsing.
- Show frame rate or message cycle.
- Apply channel and ID filters.
- Bold highlighting of changing message bytes.
Experience comprehensive monitoring of CAN bus performance with detailed statistics, displayed conveniently in panels or graphs using system variables.
- Default recording format is BLF, with the ability to convert to ASC or MAT formats later.
- Options to automatically start recording to the hard disk upon analysis startup, eliminating the risk of oversight.
- Choice for unlimited recording.
- Automatic file splitting after recording 5 million messages or reaching 500MB per file.
- Customizable naming rules, allowing inclusion of username, system time, startup time, project name, etc.
- Supports BLF/ASC formats and offers online and offline playback options.
- Offline playback functions similarly to direct opening, allowing for post-processing functions and playback range selection.
- Supports common video formats like MP4, AVI, WMV, and more.
- Can be linked to the bus playback engine.
- Configure time offset for synchronized video and bus data analysis.
- Flexible Y-axis configuration with support for multiple and separate display modes.
- Precise data point display instead of fuzzy curve shapes.
- X and Y-axis cursors for detailed data analysis.
- Abundant shortcut keys for quick graphic attri-bute adjustments.
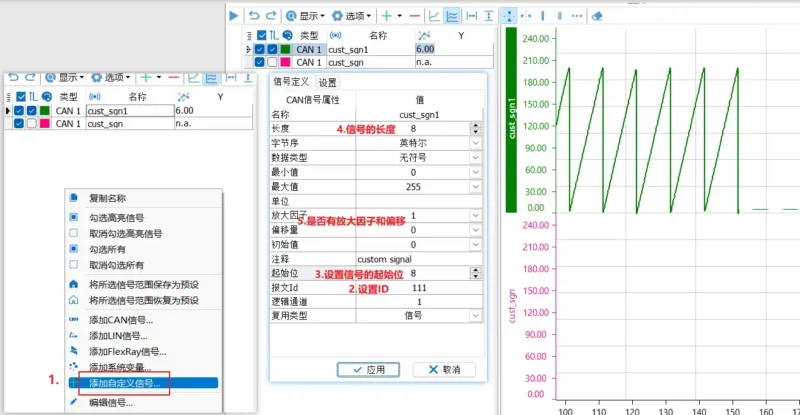
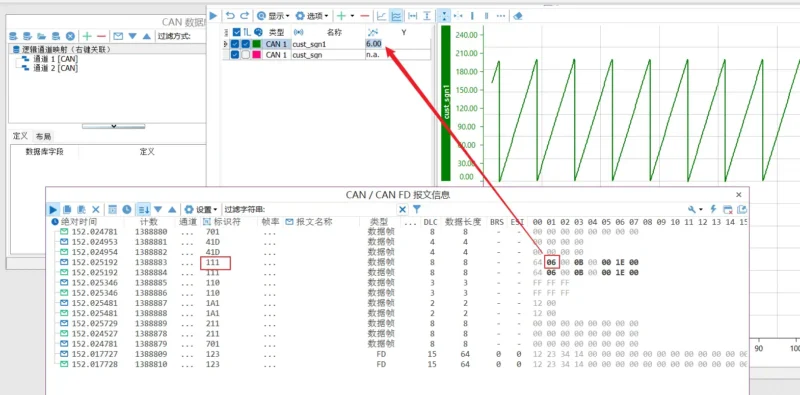
- Load DBC, ARXML, LDF, XML databases.
- Display database structure view, signal commu-nication matrix view, and message communica-tion matrix view.
FAQ
How can CAN messages be transmitted?
There are various methods to send CAN messages, including:
- Manual sending
- Shortcut key sending
- Periodic sending
- Adding custom messages and retrieving sending messages from the database
- CAN RBS simulation sending
- C script sending, which includes:
- Single-frame sending function
- Periodic sending function
- Sequence sending module
How can messages be filtered?
There are several methods for message filtering, including:
1. Message ID filtering
2. String filtering
3. Filter settings within measurements
4. Programmable filters
Why do the other three CAN channels loaded with individual DBC files on the same device disappear when reopening the software, leaving only the DBC of the first CAN channel saved?
The issue with only one DBC file being loaded by default for all four CAN channels was due to the customer using the same database network name for each channel. This resulted in a conflict where the software could only load one DBC file associated with that network name.
The problem was successfully resolved by modifying the network names for each CAN channel. By assigning unique network names to each channel, the software was able to differentiate between the DBC files and load them correctly, allowing for the intended functionality with multiple DBC files for different CAN channels.
What is the maximum delay time supported for LIN message sending?
The maximum supported time is 255ms, and this limitation is by design due to hardware constraints.
Does TSMaster support sending LIN error frames?
The active sending of error frames is a feature related to LIN interference, and it is currently not supported
What could be the reason for encountering an error when deploying a schedule table, while there are no errors when sending messages individually?
The verification algorithm in the node ECU contains an error, leading to a verification error when the schedule table is executed. This is an expected outcome. However, during single-frame message transmission, verification is intentionally not performed as part of the design, which is why no errors are triggered in that scenario.
What could be the cause of continuous FlexRay message errors and unable to communicate normally?
Continuous FlexRay message errors and the inability to communicate normally may be attributed to channel configuration issues. To address this, it is advisable to follow these steps:
Verify that there are at least two or more cold-start nodes within the network.
Ensure that there are no conflicting messages being sent between nodes.
These are among the most frequent causes of communication failures reported by most customers.
Why are the FlexRay signals not being received by the tested ECU or the entire vehicle, even though FlexRay communication is functioning normally, and the signals are being sent as expected?
There is a significant likelihood that this particular signal may require end-to-end (e2e) verification to ensure proper reception and functionality.
How to select and copy one or more signals in the graph to another graph window?
You can hold down the ‘shift’ or ‘ctrl’ key to select multiple signals and, while keeping the ‘shift’ or ‘ctrl’ key pressed, drag them to another graph window using the left mouse button.
Can you replay the messages?
Yes. The bus playback window can replay CAN, CAN FD, LIN, FlexRay, and Automotive Ethernet messages from external log files in BLF file format. We provide both offline replay and online replay functions.